I did a little more research, and this is what I came up with.
Quote:
If an event occurs N times (for example, a coin is flipped N times), then the binomial distribution can be used to determine the probability of obtaining exactly r successes in the N outcomes. The binomial probability for obtaining r successes in N trials is:
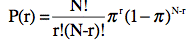
where P(r) is the probability of exactly r successes, N is the number of events, and (pi symbol) is the probability of success on any one trial. This formula assumes that the events:
(a) are dichotomous (fall into only two categories)
(b) are mutually exclusive
(c) are independent and
(d) are randomly selected
|
Taken from HyperStat Online
__________________
"We must have waffles. We must all have waffles, forthwith. Oh, we must think.
We must all have waffles and think, each and every one of us to the very best of his ability."
-- Professor Goldthwait Higginson Dorr, Ph.D.
Last edited by FleaCircus; 05-03-2004 at 06:11 PM..
|